Product designers use this stress strain diagram during material selection and structure design calculations.
Stress strain for ceramic plastics metals.
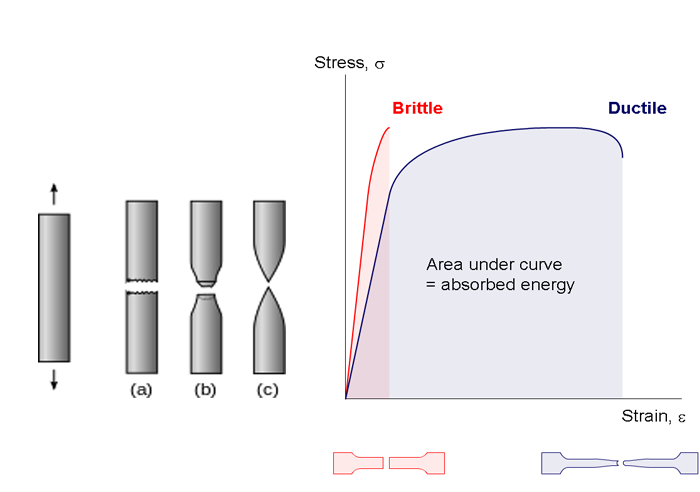
Examples of two brittle materials that fracture before entering the plastic deformation region are aluminum oxide and glass as shown in the figure below.
After plotting the stress and its corresponding strain on the graph we get a curve and this curve is called stress strain curve or stress strain diagram.
E stress strain σ ε f n a dl l o 4 where.
E young s modulus n m 2 lb in 2 psi.
Stress is proportional to load and strain is proportional to deformation as expressed with hooke s law.
Polymers exhibit a wide range of stress strain behaviors as shown in the figure below.
And finally analogous to ceramics are the stiff fibers and rigid plastics.
Elastomers are the ones that strains more w a lower stress.
Stress the term stress s is used to express the loading in terms of force applied to a certain cross sectional area of an object from the perspective of loading stress is the applied force or system of forces that tends to deform a body.
The brittle polymer red curve elastically deforms and fractures before deforming plastically.
Most metals deforms proportional to imposed load over a range of loads.
Flexible plastics behave similarly to metals although w a greater plasticity.
Occurs when noticeable necking starts ceramics.
In this the stress is plotted on the y axis and its corresponding strain on the x axis.
1 metals al alloy stress strain curve.
The blue curve is a plastic polymer and is similar to curves for many metals.
Stress strain curve of a material represents material behavior when an external force is applied.
In this article we will discuss engineering and true stress strain curve for ductile and brittle materials.
Stress strain curve is the plot of stress and strain of a material or metal on the graph.
Occurs when crack propagation starts polymers.
T tmelt 3 simple tension.
With a very short elastic region but highly capable of supporting huge stresses.
In engineering and materials science a stress strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain it is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation from which the stress and strain can be determined see tensile testing these curves reveal many of the properties of a material such as the young s modulus the yield strength.
Its behavior begins in the linear elastic deformation region.
Occurs when polymer backbones are aligned and about to break σ y engineering typical response of a metal ts stress engineering strain plastic permanent deformation at lower temperature.